Digital skills are becoming an increasingly frequent part of our working lives. The ability to use technology is a vital requirement in many roles due to increased adoption of software to increase business efficiency and customer experience. With more time at work spent on technology than ever, a large number of psychological studies have investigated the effects of learning and using digital skills over recent years. Read on to find out about developing your digital skills, the psychological benefits and avoiding the disadvantages that come with using technology at work.

What are Digital Skills?
Foundational digital skills start with the basics of being able to turn on a computer or access the internet. Next are skills like searching for information on the internet, writing an email, or creating a simple document, such as a CV or resume. The level above is the ability to transfer skills to different contexts or platforms, such as accessing information in different databases, or setting up data for others. These transferable skills are called ‘digital literacy‘. These skills enable you to learn new software and technology quicker.
An article by UNLV on digital skills provides a good definition showing the extent of abilities involved in the current workplace and business environment:
Essential Digital Skills
Following on from this definition, the Digital Marketing Institute lists 10 essential digital skills for employability in 2023:
- Social Media
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM)
- Data Analytics
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Mobile Marketing
- Strategy and Planning
- Social Selling
- Pay-Per-Click Marketing (PPC)
- Video
As you can see from this list, being able to ‘find, evaluate, use, share and create content using digital devices‘ are crucial skills in today’s workplace. The list of skills above increases your employability in today’s employment market, because many businesses use content creation and online marketing to reach their audience.
With all of these skills, and many more, there is a rapidly growing number of software that can meet the needs of businesses. Read this guest post about ‘6 Steps to Choosing the Right Software‘ if you are interested in the decision-making behind finding the right software for your work needs.
Why Digital Skills are Important
Demand for Digital Skills
It has been projected that work hours using basic digital skills will increase by 69% in the US and 65% in Europe by 2030 (McKinsey Global Institute, 2018). This is due to increased automation and growth in demand for digital skills, even in professions that previously did not rely on digitalisation.
One example of this is home health aides in the US, who previously required very little digital skills. But their work is becoming more digital as software is being used to keep records and share information between related professionals. Between 2002 to 2016, the digital content score (including scores for digital knowledge, importance of digital use and frequency) for home health aides increased from a score of 3 to 23 (Muro et al, 2017).
Scores for digital content are increasing across a wide range of professions, including teaching, healthcare and human resources. For more insights on the increase and importance of digital skills for career progress, read this fascinating article from the Urban Institute (Hecker and Loprest, 2019).
The top 20 job roles that are increasing in demand in the workplace, according to ‘The Future of Jobs Report 2020′, are all dependent on technology-based skills (see the image below).
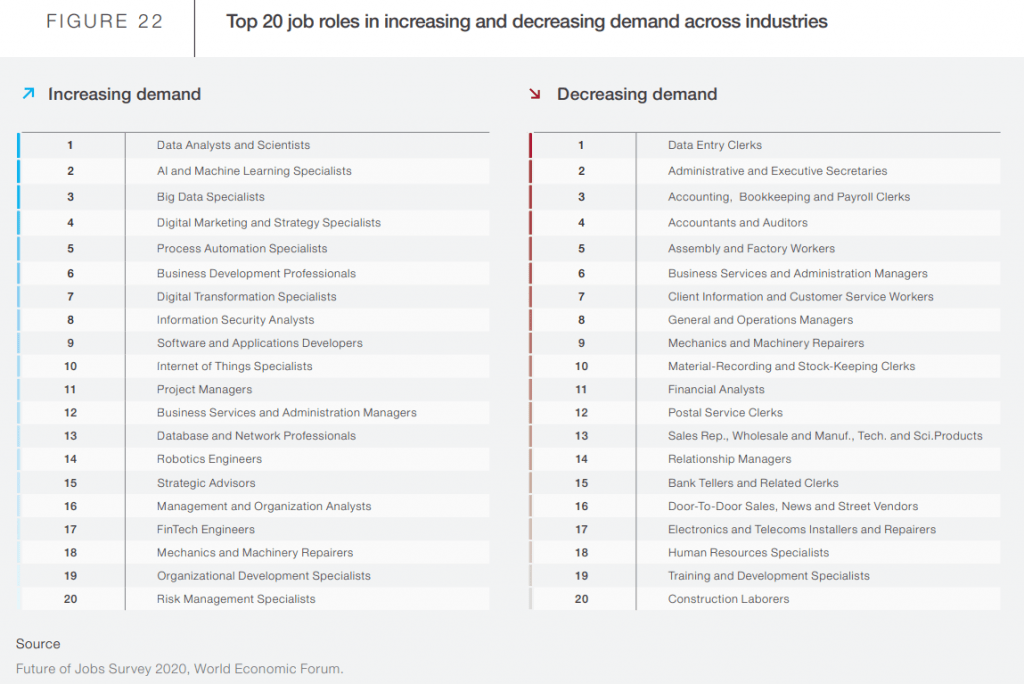
In a recent study of digital competencies and job performance, researchers found that digital competencies increased job performance and psychological empowerment of employees (Pacheco and Coello-Montecel, 2023). Therefore, having a good level of digital skills is important for your own positive feelings at work, and the success of your company.
Digital Skills at Work
CV/Resume/Applications
The majority of companies now expect to receive a digital version of your CV/resume and/or application. This demonstrates your skills and ability to follow their application process. It also makes it a lot easier for employers to sort applications as they can run the digital files through an Applicant Tracking System (ATS). ATS is a software that collects and sorts resumes according to how closely they match the input job description.
Interview
Talking about your digital skills and how they are relevant or transferable to the job role in an interview can demonstrate your prior learning, experience and willingness to continue to learn. You can also ask questions about their current software and what training is available to support your further learning.
Self-employment/Freelance
Digital skills can enable you to work remotely, keep track of your invoices, receipts and accounts, and schedule your work to post automatically, along with many more uses. Software can reduce time spent on tasks, increase your reach, and add to the professionalism of your service or products.
Businesses
In order to compete, and gain the benefits of software relevant to your industry, it is crucial that businesses select software carefully. For a step-by-step guide to this selection for your business, read this article next.
Changing Career
With better digital literacy, you are better able to transfer skills and learn the new technologies quickly for a career pivot. There will be more opportunities open to you in the current job market. You will also be better equipped if you choose to start your own business, taking advantage of the relevant technologies available.
Ways of Learning Digital Skills
There are several ways of gaining the digital skills you need to be digitally competent:
- Self-learning: experimenting with trial and error, watching videos, tutorials, reading how-to articles etc. You could set up a YouTube channel, write a blog, podcast, sell items, get creating and share posts on social media etc. There are many ways you can practice your digital skills for fun or as a hobby, learning as you go. You can then use these as examples when you come to apply for jobs, or have the skills ready for starting and marketing your own business.
- Free or paid for courses: because digital skills are vital in the workforce, there are many free courses online and in adult education settings, especially to support you in the beginner levels. Many local libraries also offer support with getting started.
- On the job: beyond the foundational skills level, you can transfer your skills to learning new software and technologies as you work. Employers will usually provide training for their chosen software, or you can ask for further training or funding to support your learning.
Benefits of Developing Your Digital Skills
Benefits to Individuals
Alongside many other benefits of workplace technology, here are a few advantages for you as an individual found by the psychological research:
- development of new transferable and meaningful skills (Maisiri et al, 2019)
- improving creativity and innovation (Oldham and Da Silva, 2015)
- feelings of empowerment, being heard on social media and part of the decision-making (Li, 2016).
- positive association with job satisfaction (Bolli and Pusterla, 2022)
Avoiding the Disadvantages
With the advantages of using technology in the workplace, there have been found to be psychological disadvantages too, including:
- increased stress, burnout and mental health issues (Berg-Beckoff et al, 2017)
- overload (Lee et al, 2016)
- impacts on work-life balance and blurred boundaries (Barriga Medina et al, 2021)
- less productivity due to distractions (Ali-Hassan et al, 2015)
To avoid these disadvantages, it is important to set clear boundaries on the use of technology at work and at home. It is also useful to continue to develop your digital skills to be able to use software to your advantage at work for making tasks easier and more efficient. Try to avoid multi-tasking, by having just one piece of software or social media open at a time. Ask for support and further training from your employer or seek your own learning in the areas that will benefit your work the most.
Conclusion
Technology is a wonderful tool that is increasingly used in the workplace because of the advantages it provides to businesses and individuals. Therefore, demand is increasing for digital skills competency in applicants and employees.
Research has found many benefits to learning digital skills, as it can increase our interest in our work, our creativity, our sense of empowerment and our job satisfaction. However, research has also found the disadvantages of this increased use of technology at work can lead to stress, burnout, overload, unbalanced work-life boundaries and less productivity. If we want to get the balance with technology and our mental health right at work, develop your digital skills, but set boundaries. This will help you to minimise the disadvantages and gain the advantages of those digital skills.
References:
Ali-Hassan, H., Nevo, D., & Wade, M. (2015). Linking dimensions of social media use to job performance: The role of social capital. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24(2), 65-89.
Barriga Medina, H. R., Campoverde Aguirre, R., Coello-Montecel, D., Ochoa Pacheco, P., & Paredes-Aguirre, M. I. (2021). The influence of work–family conflict on burnout during the COVID-19 pandemic: The effect of teleworking overload. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(19), 10302.
Berg-Beckhoff, G., Nielsen, G., & Ladekjær Larsen, E. (2017). Use of information communication technology and stress, burnout, and mental health in older, middle-aged, and younger workers–results from a systematic review. International journal of occupational and environmental health, 23(2), 160-171.
Bolli, T., & Pusterla, F. (2022). Decomposing the effects of digitalization on workers’ job satisfaction. International Review of Economics, 69(2), 263-300.
Hecker, I., & Loprest, P.J. (2019). Foundational Digital Skills for Career Progress.
Lee, A. R., Son, S. M., & Kim, K. K. (2016). Information and communication technology overload and social networking service fatigue: A stress perspective. Computers in human behavior, 55, 51-61.
Li, Z. (2016). Psychological empowerment on social media: who are the empowered users?. Public Relations Review, 42(1), 49-59.
Maisiri, W., Darwish, H., & Van Dyk, L. (2019). An investigation of industry 4.0 skills requirements. South African Journal of Industrial Engineering, 30(3), 90-105.
McKinsey Global Institute (2018). Skill Shift: Automation and the Future of the Workforce. New York: McKinsey Global
Institute.
Muro, Mark, Sifan Liu, Jacob Whiton, and Siddharth Kulkarni. 2017. Digitalization and the American Workforce.
Washington, DC: Brookings Institution.
Oldham, G. R., & Da Silva, N. (2015). The impact of digital technology on the generation and implementation of creative ideas in the workplace. Computers in human behavior, 42, 5-11.
Pacheco, P. O., & Coello-Montecel, D. (2023). Does psychological empowerment mediate the relationship between digital competencies and job performance?. Computers in Human Behavior, 140, 107575.
